Official Independent Contractor Pay Stub Form
The Independent Contractor Pay Stub form is a document that outlines the earnings and deductions for individuals working as independent contractors. This form provides a clear summary of the payment details, ensuring that both the contractor and the hiring entity have a record of the financial transactions. For those looking to fill out this form, please click the button below.
Access Independent Contractor Pay Stub Editor
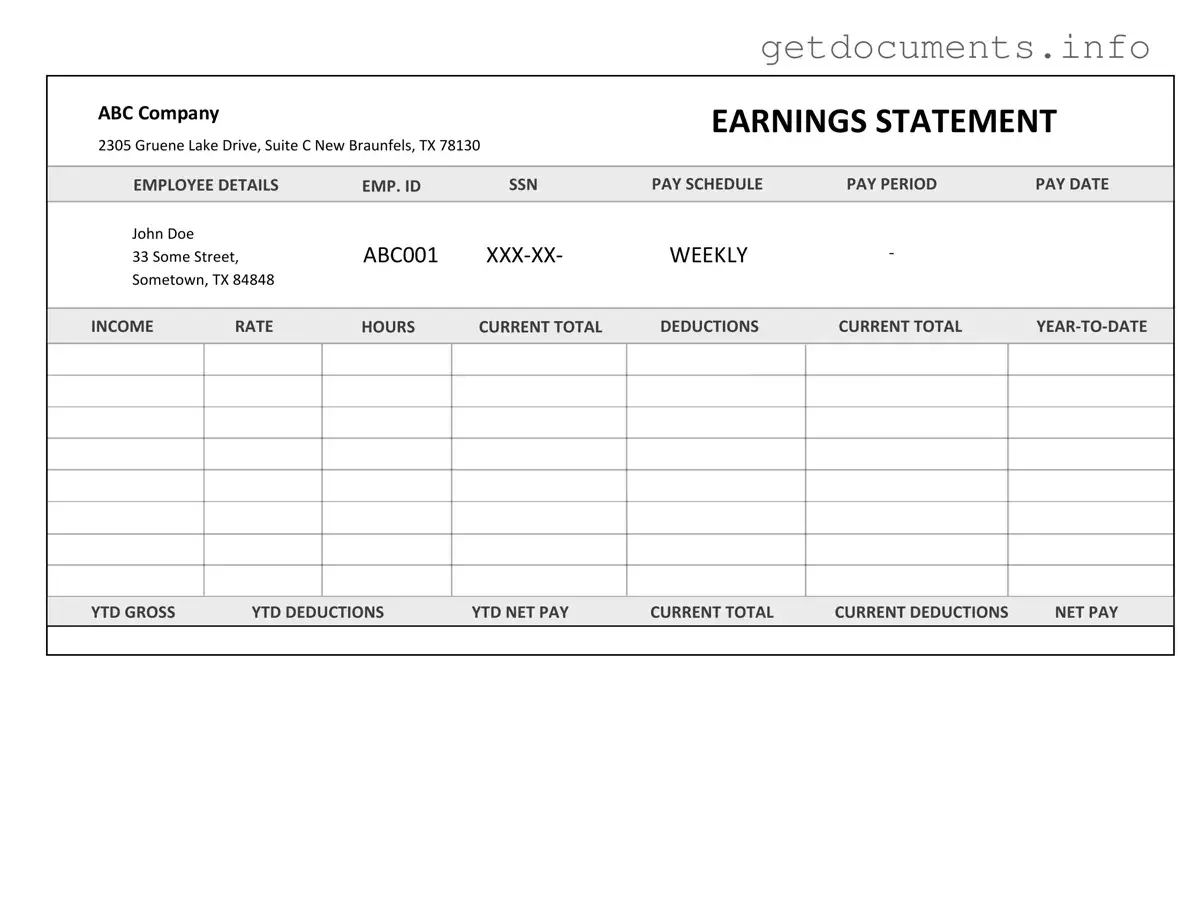
Official Independent Contractor Pay Stub Form
Access Independent Contractor Pay Stub Editor
Got places to be? Complete the form fast
Fill out Independent Contractor Pay Stub online and avoid printing or scanning.
Access Independent Contractor Pay Stub Editor
or
⇩ PDF File
